Landing Pages
We use landing pages throughout our Business Design Process to understand, communicate and validate our ideas. Let's learn more about how to structure a landing page and some important best practices.
Content
1. Overview
A landing page is a standalone web page that a person "lands" on after clicking through from an email, ad, or other digital location. Once they're on your landing page, users are encouraged to take an action, such as joining your list or buying your products.
Landing Pages are a great tool to validate critical assumptions of your business model (e.g. sales channels, pricing, brand & message). You can do that even without having the product ready and on the market (with "Fake-Door testing"). But you can also use landing pages very early in the design process to get a better understanding of your idea within your team and to communicate your idea in a tangible and visual way. You can use it as a tool to...
...help you as a team to develop a common understanding of your idea
...help you see and understand your idea from the customers perspective
...help you as a team to think through the details of your idea (benefits, target group(s), pains & gains, brand & message...)
...help you develop a structured story / sales pitch for your idea
...help you to communicate your idea to potential stake-holders (customers, sponsor...)
...help you to get a first impression how your idea could "feel" like when you are on the market
...help you to get other people excited for your idea
...to validate critical assumptions of your business model (e.g. sales channels, pricing, brand & message...)
2. Key Elements
Cover
The cover area is the most important part of our landing page. It's the first thing users will see when they visit your site. Within a couple of seconds a user will decide to stay and learn more about what you’re offering — or not. See "Brand & messages" and "Primary Target Group" in our Business Model.
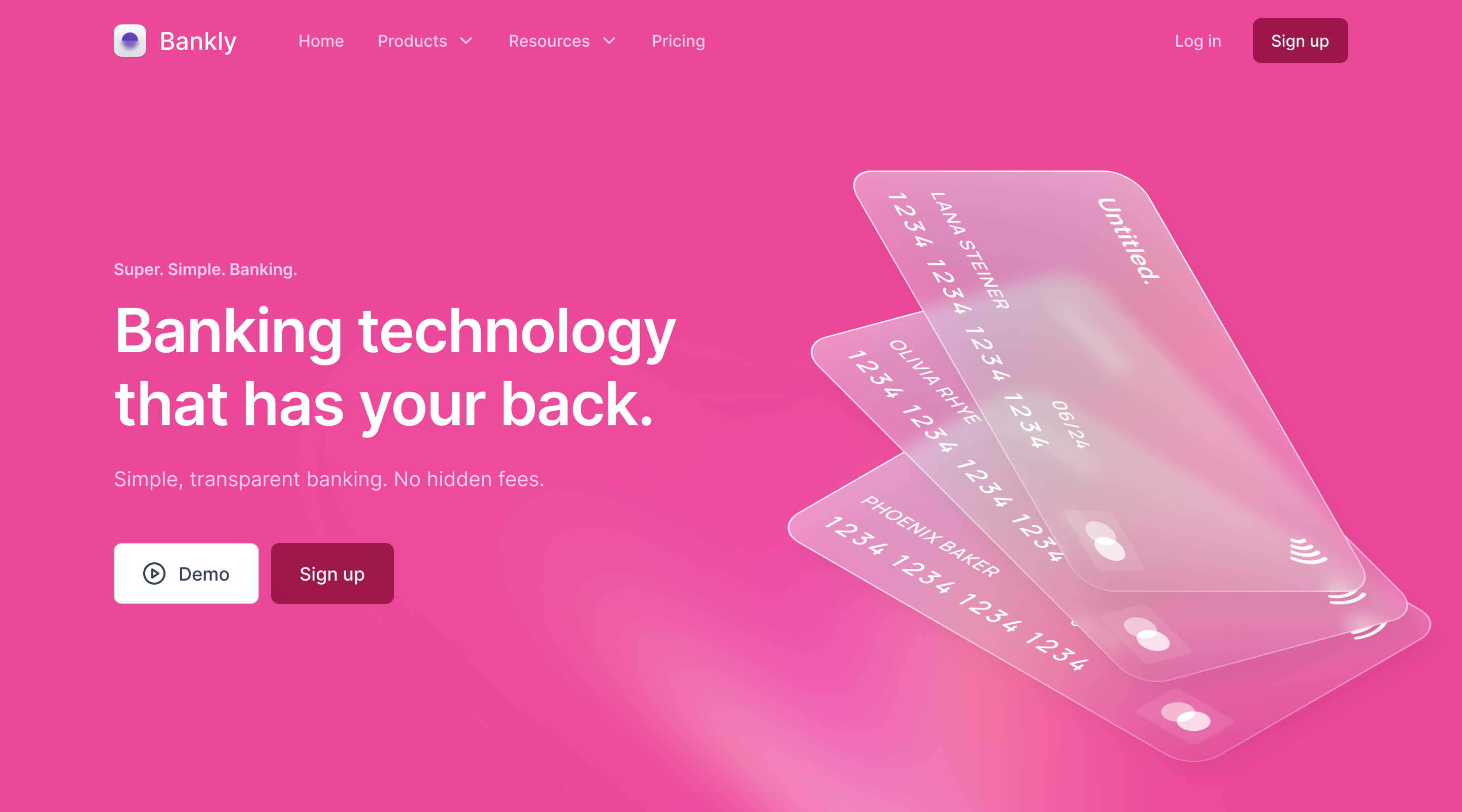
Best Practices
If you do online ad campaigns to drive traffic to your landing page, make sure the headline corresponds to the text from your ads
Make sure to make the font of the headline larger than any other font
Don't use too much text in your headline
Use a benefit-oriented headline
Put a call to action in the cover area
Use an image (or a video) which engages your primary target group emotionally and fits your brand and product/service
Offering
In this area you can describe what your offering actually looks like (what you do) and which problem you solve. In this section the visitor of your page needs to understand if you can help him to get his job done. See "Offerings" and "Job(s) to get done" in our Business Model.
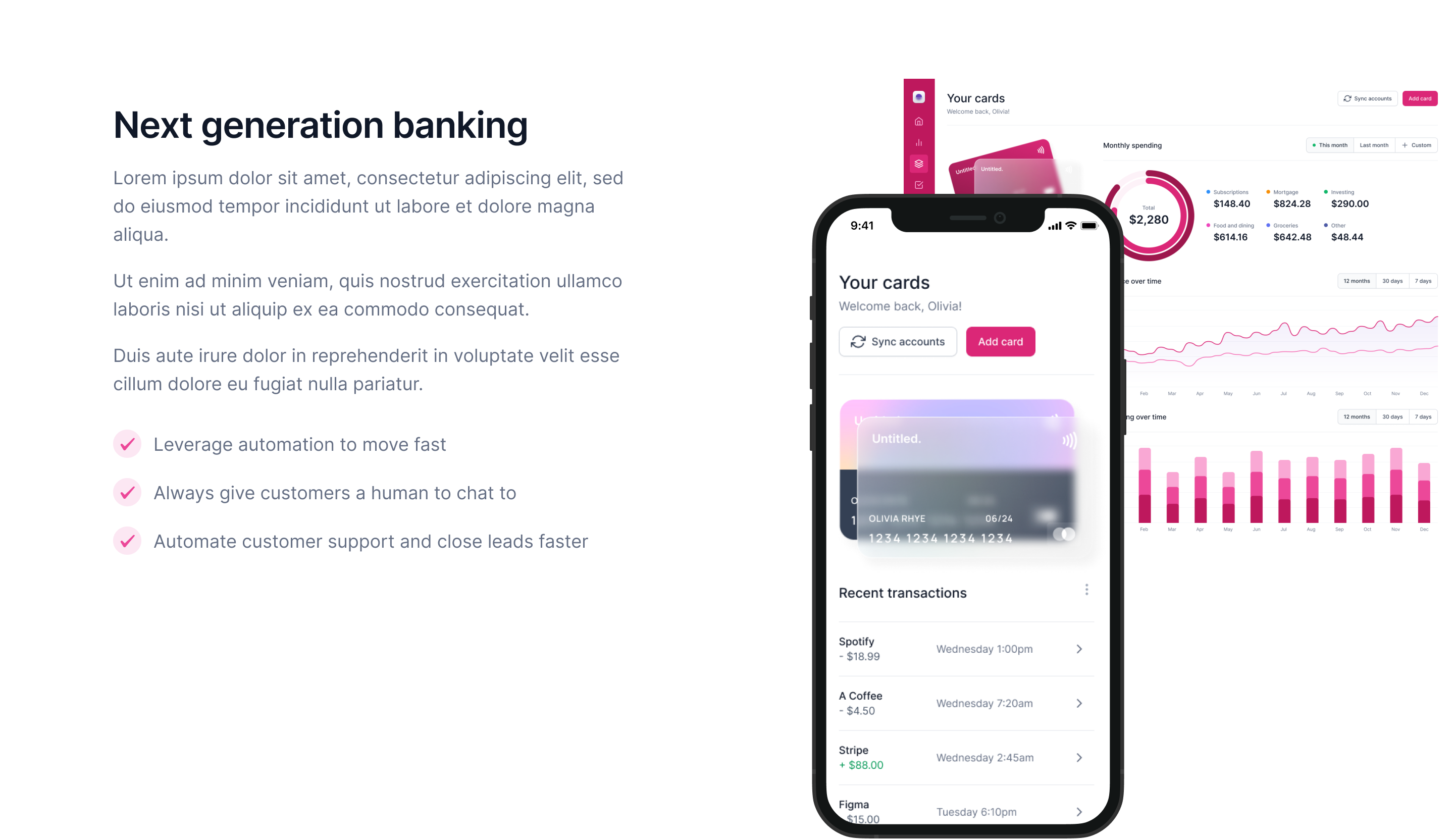
Best Practices
Be very precise and on point in you language. There is not much room to describe what you do.
Use bullet points to summarize your offering
Use images/drawing/screenshots to visualize your offering
Benefits
In this area we describe how the product or service will help our primary target group to get their job(s) done. Customers aren't just interested in what the product or service is but also what they gain from it. See "Pains & Gains", "Job(s) to get done" and "Core Value" in our Business Model.

Best Practices
Make sure you talk about benefits, not features
Focus on a maximum of four key benefits
Add visual elements (e.g. icons) which amplify the benefit
Don't use too much text
Solution or process
Here we describe how our solution works and what the users need to do to experience the benefits of our product or service. See "Offering" in our Business Model.
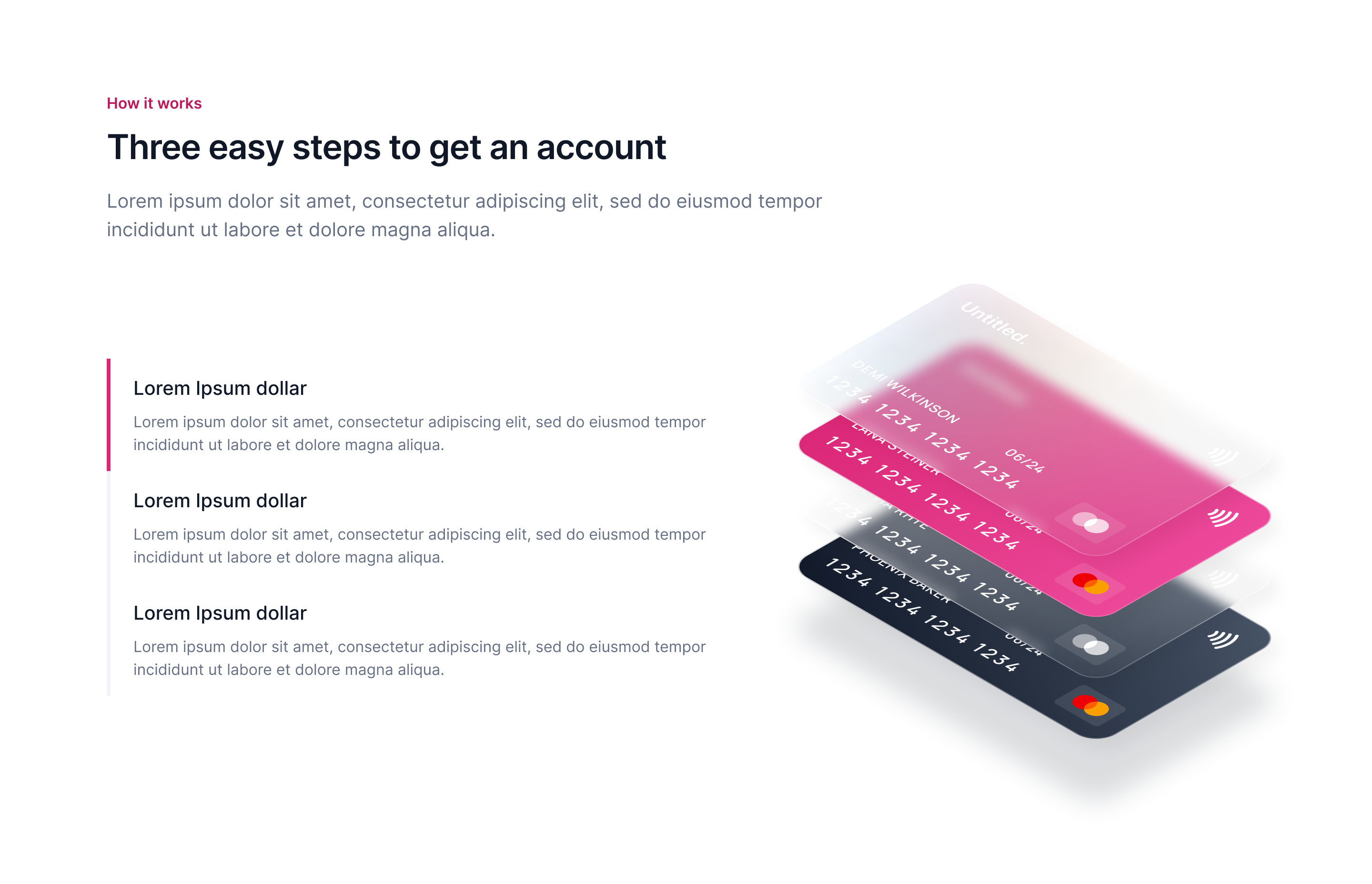
Best Practices
Describe what happens in simple steps (1., 2., 3,...)
Visualize steps with icons or screenshots of your product
If your product is more complex, simplify the representation for the landing page
Testimonials
With testimonials we can show some social proof in our product or service. Recommendations from trusted users play a big role in purchase decisions. See all parts of our Business Model.

Best Practices
Include personal details (full names, job titles, place of residence etc.)
Use pictures of your users (it helps to build trust)
Use testimonials from people who are most relevant to your primary target group
Be very specific about features, benefits etc.
Team
In this section it's time to talk about yourself. This will built trust in your product or service and shows that the people behind the product are experts in the field.
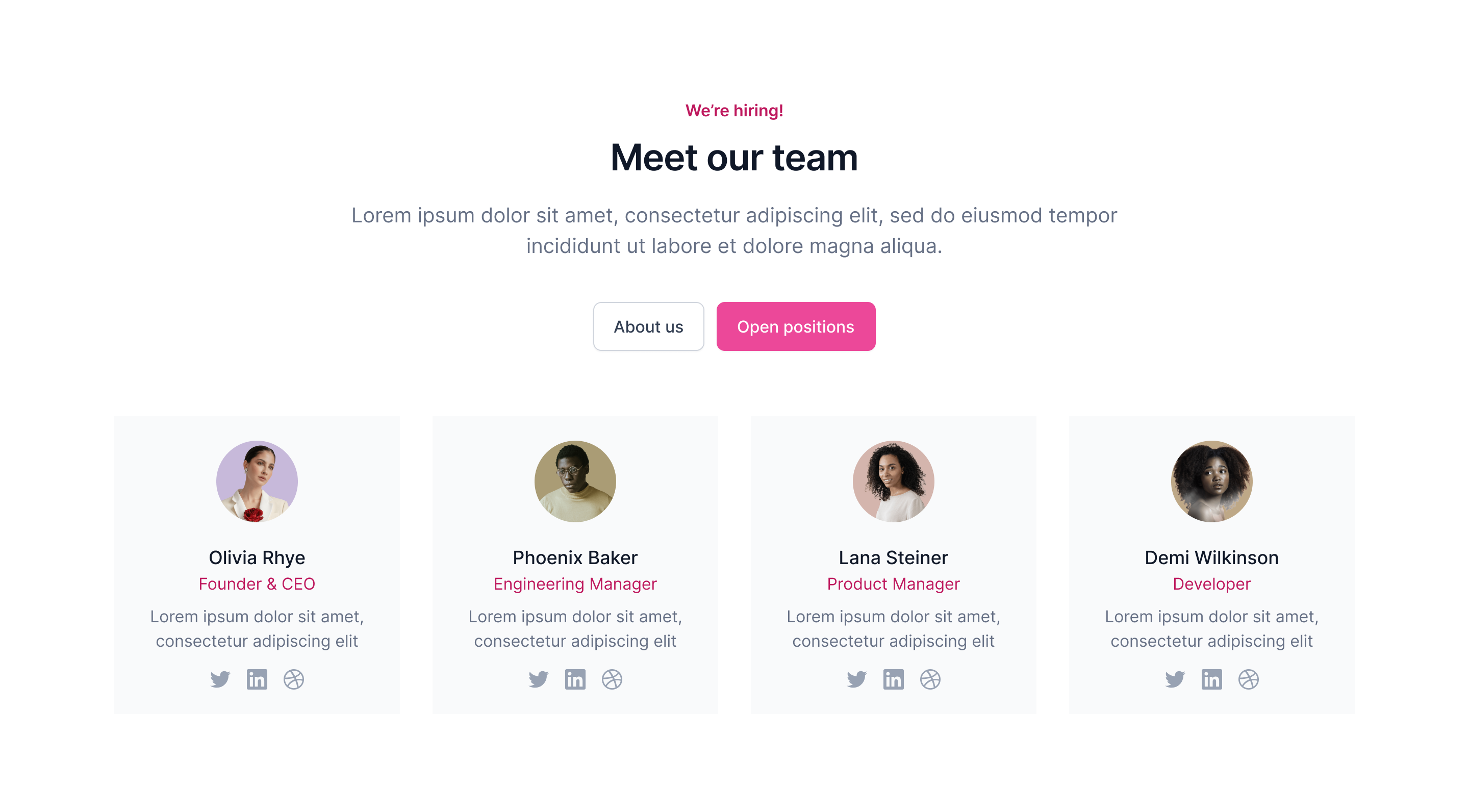
Best Practices
Include pictures of yourself
Add contact options (LinkedIn, Email...)
Show what role you have within the company
Call to action
This is the area where we show our users what we want them to do (signup-form for our product, download, configurators, register for newsletter etc.). Your call-to-action buttons should point to this area. See "Offering" in our Business Model.

Best Practices
Tell your users exactly what to do
Highlight what your users get
If you can, show your product in action (it helps users imagine themselves as your customer)
Use it all over your page
3. Optional Elements
Pricing
Here we talk about our pricing options and plans. See "Profit formula" in our Business Model.
Best Practices
Simplicity wins
Highlight the benefits
Use urgency messages
Highlight call to action
Help to compare
Highlight the best option
FAQ
FAQs help to anticipate potential customer questions and clarify critical points of your product or service.
Best Practices
Use an accordion to save space
Address the fears, uncertainties and doubts (friction points)
4. Investments
When you are looking at user behavior on a landing page, consider different levels of investments of users to track how committed they are (see Customer Investments).
Possible "investments" are:
Data Point | Level of Investment |
User clicks "order now" button or enters credit card details | ++++++++++ |
User enters personal data | ++++++++++ |
User enters his email (E.g. Newsletter) | ++++++++ |
User contacts us via contact form or chat | ++++++ |
User uses configurator | ++++++ |
User downloads info material | ++++ |
User scrolls the page (scroll depth) | ++++ |
User clicks "show more" button | +++ |
User views teaser video | +++ |
5. Usage Scenarios
Explore open questions from your Hypotheses & Experiments template
Validate hypotheses from your Hypotheses & Experiments template
6. Example Tools
7. Instructions for Coaches
For high resolution stock photos, you can use free websites like Pexels and Unsplash or alternatives like iStock and Shutterstock for payed content.
Discuss in your team which colors best fit to your offering. Color palettes and gradients can be found on plenty websites, such as Adobe Color and UI Gradients. For color shading use Hex Color Tool.
Think about it if it is better to present your offering on-brand or off-brand and prepare your landing page accordingly.
Landing pages are a great way to conduct A/B tests in case you want to test two versions of your offering with different features, pricing, etc.
Our prototyping engineers build landing pages in hours – not days! That allows you to focus on the content and the corresponding experimental setup. Please contact us if you need support.
If your team is technically savvy (HTML, CSS) or gets support from prototyping engineers, ready made templates are a great way not to start from scratch (e.g. from ThemeForest). Choose a template that includes the best preview options for your product / service and everything you need to set up your call-to-action button or contact form. We recommend to choose a responsive template to save your time.
If your team is not familiar with HTML / CSS, visual web-page builders (like Wix or Launchrock) allow them to setup their own landing page very quickly based on templates. But be aware that from our experience, these tools can kill your time when you want to change more than just text, pics and colors.
If your using a landing page to validate a hypothesis, make sure that your team gets together and prepares the content based on your research design. Don't forget to setup an ad campaign or other promotional campaigns to get traffic on your landing page and install tracking mechanisms to monitor user behavior if needed.
8. Miro Board
We developed a miro board which helps teams build their landing pages. Drop us a line, if you need editing rights to use it in your own workshops.
Have a look at it: https://miro.com/app/board/uXjVO6pcwLU=/
